Question
- Leaving Certificate Physics (Higher) 2023: Section B Q12 (a)
- Back to the question >
Answer
Anti‐matter is the most expensive substance on Earth, costing about €65 trillion per gram.
(i) What is anti‐matter?
Anti-matter is made from anti-particles. For every category of particle, there also exists the equivalent anti-particle. When particle and anti-particle meet, they are annihilated and their mass is converted into other forms of energy.
(ii) Who made a mathematical prediction of the existence of anti‐matter?
Dirac
A positron is an example of anti‐matter.
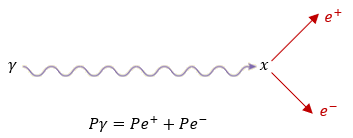
(iii) Write an equation to show the pair production of an electron‐positron pair.
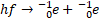
(iv) Explain how:
(a) charge is conserved in this interaction,
The total charge before this reaction occurs is zero. The total charge after is also zero (+1 -1 = 0). In this way, the total charge has been conserved.
(b) momentum is conserved in this interaction.
The total momentum before the interaction is the momentum of the photon (a gamma ray, represented by ‘hf ’). The vector sum of the momentum of the two particles created immediately after they are created will equal that of the photon.
(v) List the fundamental forces, in order of increasing strength, that a positron experiences.
Gravitational
Electromagnetic
Strong nuclear
(vi) Name the fundamental force that a positron does not experience.
Weak nuclear
(In general, positrons do not experience the weak nuclear force)
In the Large Hadron Collider researchers are investigating the pair annihilation of a proton anti‐proton pair.
(vii) Calculate the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation produced when a proton and an anti‐proton annihilate.
When a proton and anti-proton collide, they create two gamma rays:
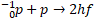
Total mass converted:
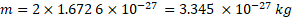
Energy converted:
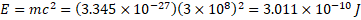
Frequency of gamma ray:
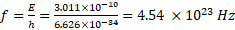
Wavelength:
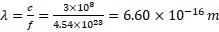
(viii) Hadrons can be classified as baryons or mesons. Distinguish between baryons and mesons.
Baryons contain 3 quarks or anti-quarks.
Mesons contain one quark and one anti-quark.
(ix) State the quark composition of
(a) a proton: up, up, down
(b) an anti‐proton: anti-up, anti-up, anti-down
(x) The Large Hadron Collider is an example of a modern particle accelerator. Explain how it differs from the particle accelerator used by Cockroft and Walton.
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is a circular particle accelerator, consisting of a circular tube many kilometres long. Particles (often protons) move around this circular path many times before being involved in a collision. This allows them to build up enormous speeds and energy.
The Cockroft and Walton equipment was linear. The protons moved through a path that was only a few metres long. In comparison to the LHC, the energy involved was much smaller.
