Question
- Leaving Cert. Biology (Higher) 2009: Q14
- Back to the question >
Answer
14.
(a)
(i)
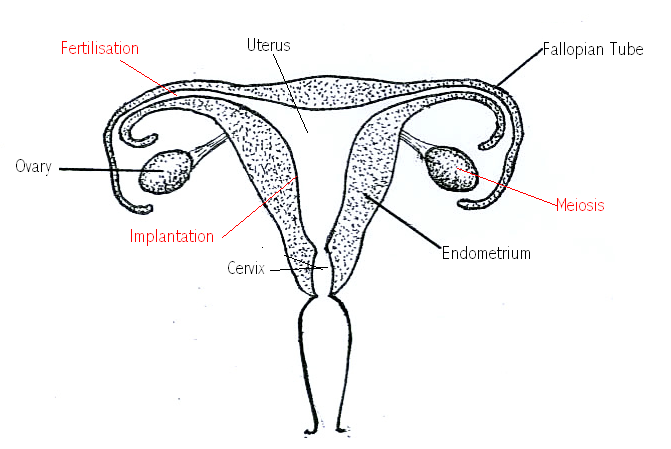
(ii) Oestrogen is produced by the graafian follicle as it develops in the ovary. It is produced during days 5 to 14 and causes the endometrium to develop. It also inhibits follicle-stimulating hormone ensuring that no more eggs develop. Oestrogen reaches its highest level just before day 14 and this stimulates the release of Lutenising Hormone, which causes ovulation.
(iii)
1. Fibroids are tumours of the uterus. It is not known for certain what causes fibroids but they may be an abnormal reaction to oestrogen.
2. Small fibroids are not normally treated and larger ones are removed by surgery. Sometimes, it may be necessary to remove the entire uterus.
(b)
(i) The placenta is fully formed at about three months into the pregnancy. It allows gases, nutrients and waste to pass between the mother and the embryo. The blood of the embryo does not mix with the mother’s blood but the placenta allows the exchange of material between them. It is important that the bloods do not mix because the blood pressure in the mother is much higher and also it is possible for the embryo to have a different blood group to the mother.
(ii) The placenta is formed from the chorionic villi of the embryo and the blood vessels of the mother in the endometrium.
(iii) The placenta stops producing progesterone, which causes the uterus to start to contract. The pituitary releases oxytocin, which also causes the uterus to contract. In stage 1 the contractions of the uterus push the foetus towards the cervix and the pressure causes the membranes to rupture and the amniotic fluid to drain out - ‘waters breaking’. In stage 2 the cervix dilates and the foetus is pushed out through the cervix and vagina. The cord is clamped and cut. Stage 3 involves the uterus contracting to release the placenta and membranes.
(iv) In-vitro fertilisation is when fertilisation occurs outside of the body.
(v) A morula is a solid clump of cells formed about 3 days after fertilisaton.
A blastocyst is a hollow ball of cells formed around day 5. The outer layer of the blastocyst forms the membranes while the inner cells form the embryo.
(c)
(i) Rhizopus
(ii) Fungi
(iii)
A = Sporanagiophore
B = Sporangium
C = Spores
(iv)
1. It is used to absorb food.
2. Rhizpous secretes enzymes on the food source, which digest the food. The rhizoids increase the surface area to make absorption of the nutrients more efficient.
(v) Saprophytic
(vi) Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelle. They are larger than prokaryotic cells.
(vii) Prokaryotic
(a)
(i)

(ii) Oestrogen is produced by the graafian follicle as it develops in the ovary. It is produced during days 5 to 14 and causes the endometrium to develop. It also inhibits follicle-stimulating hormone ensuring that no more eggs develop. Oestrogen reaches its highest level just before day 14 and this stimulates the release of Lutenising Hormone, which causes ovulation.
(iii)
1. Fibroids are tumours of the uterus. It is not known for certain what causes fibroids but they may be an abnormal reaction to oestrogen.
2. Small fibroids are not normally treated and larger ones are removed by surgery. Sometimes, it may be necessary to remove the entire uterus.
(b)
(i) The placenta is fully formed at about three months into the pregnancy. It allows gases, nutrients and waste to pass between the mother and the embryo. The blood of the embryo does not mix with the mother’s blood but the placenta allows the exchange of material between them. It is important that the bloods do not mix because the blood pressure in the mother is much higher and also it is possible for the embryo to have a different blood group to the mother.
(ii) The placenta is formed from the chorionic villi of the embryo and the blood vessels of the mother in the endometrium.
(iii) The placenta stops producing progesterone, which causes the uterus to start to contract. The pituitary releases oxytocin, which also causes the uterus to contract. In stage 1 the contractions of the uterus push the foetus towards the cervix and the pressure causes the membranes to rupture and the amniotic fluid to drain out - ‘waters breaking’. In stage 2 the cervix dilates and the foetus is pushed out through the cervix and vagina. The cord is clamped and cut. Stage 3 involves the uterus contracting to release the placenta and membranes.
(iv) In-vitro fertilisation is when fertilisation occurs outside of the body.
(v) A morula is a solid clump of cells formed about 3 days after fertilisaton.
A blastocyst is a hollow ball of cells formed around day 5. The outer layer of the blastocyst forms the membranes while the inner cells form the embryo.
(c)
(i) Rhizopus
(ii) Fungi
(iii)
A = Sporanagiophore
B = Sporangium
C = Spores
(iv)
1. It is used to absorb food.
2. Rhizpous secretes enzymes on the food source, which digest the food. The rhizoids increase the surface area to make absorption of the nutrients more efficient.
(v) Saprophytic
(vi) Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelle. They are larger than prokaryotic cells.
(vii) Prokaryotic
