Question
- Leaving Cert. Geography (Higher) 2011: Part Two Q3 A-C
- Back to the question >
Answer
Isostasy refers to the vertical movement of the earth’s crust. These movements can be upwards or downwards. Isostasy is caused by changes in the surface weight on the crust or changes in the weight of the crust itself. Isostasy results in a change to land levels. These changes are relative to sea levels.
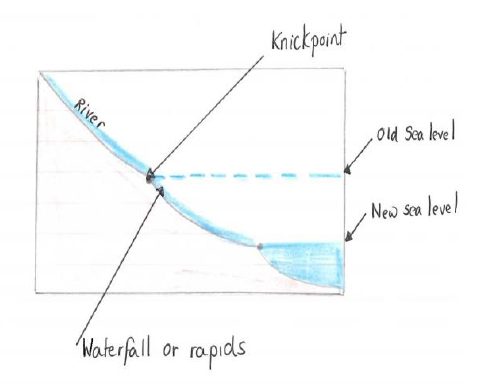
In this answer I will discuss how the effects of isostasy can be seen on Irish rivers. The base level is the lowest level at which river erosion can take place and this is sea level. Changes occurring in climate or tectonic activity may result in a rise or fall in the base level of a river. If the land level rises or sea levels fall, there is a drop in the base level. This results in new land emerging from the sea, in steepening the slope of the river and the river starting to erode again. This process is called rejuvenation. New landforms result such as knickpoints and paired terraces.
Knickpoints are small waterfalls found in the lower course of a river. They occur at the old base level, the point where the river once entered the sea. Due to isostatic uplift the sea level was lowered and the river had to travel a longer distance to reach the sea. The river was rejuvenated as it was given renewed ability to vertically erode the land in order to reach the sea. The rejuvenated river cuts a new profile for itself and the place where the new profile meets the old profile is known as the knickpoint. Knickpoints are visible on many Irish rivers in the south and east of Ireland at a height of about 150 metres above sea level. A knickpoint can be seen by the presence of a new waterfall on the River Shannon, south of Lough Derg and on the River Erne in Co. Donegal at Kathleen’s falls.
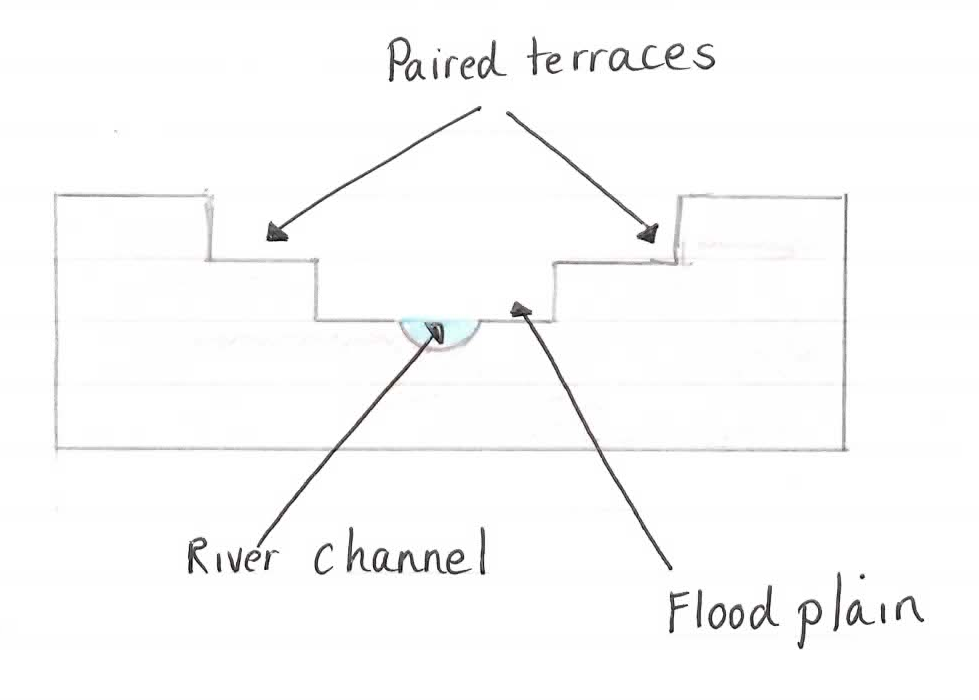
During rejuvenation vertical erosion, through the combined processes of hydraulic action and abrasion, is very effective. The river erodes the clay, silt and bedrock in its floodplain and this forms a new narrower floodplain at the lower level. The original valley floor is left high above the new floodplain and is seen as steps in the land on either side of the river of the rejuvenated river channel. These steps are called paired terraces and are often seen in pairs on either side of the river. Sometimes a river can be rejuvenated more than once and so another set of terraces are formed resulting in a river valley with stepped sides. Examples of paired terraces can be seen on the River Dodder at Terenure, Co.Dublin and on the River Barrow in Co. Kilkenny.
In this answer I will discuss how the effects of isostasy can be seen on Irish rivers. The base level is the lowest level at which river erosion can take place and this is sea level. Changes occurring in climate or tectonic activity may result in a rise or fall in the base level of a river. If the land level rises or sea levels fall, there is a drop in the base level. This results in new land emerging from the sea, in steepening the slope of the river and the river starting to erode again. This process is called rejuvenation. New landforms result such as knickpoints and paired terraces.
Knickpoints are small waterfalls found in the lower course of a river. They occur at the old base level, the point where the river once entered the sea. Due to isostatic uplift the sea level was lowered and the river had to travel a longer distance to reach the sea. The river was rejuvenated as it was given renewed ability to vertically erode the land in order to reach the sea. The rejuvenated river cuts a new profile for itself and the place where the new profile meets the old profile is known as the knickpoint. Knickpoints are visible on many Irish rivers in the south and east of Ireland at a height of about 150 metres above sea level. A knickpoint can be seen by the presence of a new waterfall on the River Shannon, south of Lough Derg and on the River Erne in Co. Donegal at Kathleen’s falls.

During rejuvenation vertical erosion, through the combined processes of hydraulic action and abrasion, is very effective. The river erodes the clay, silt and bedrock in its floodplain and this forms a new narrower floodplain at the lower level. The original valley floor is left high above the new floodplain and is seen as steps in the land on either side of the river of the rejuvenated river channel. These steps are called paired terraces and are often seen in pairs on either side of the river. Sometimes a river can be rejuvenated more than once and so another set of terraces are formed resulting in a river valley with stepped sides. Examples of paired terraces can be seen on the River Dodder at Terenure, Co.Dublin and on the River Barrow in Co. Kilkenny.

