Question
- Leaving Cert. Chemistry (Higher) 2014: Section B Q8
- Back to the question >
Answer
(a)
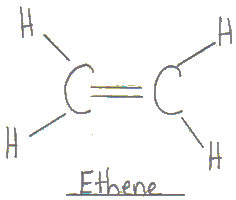
Ethene
(b)
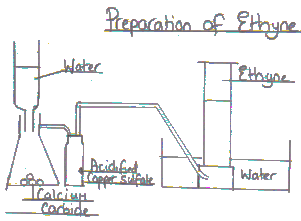
(c)
Test for unsaturation
(d)
(i) Substitution -> monochlorination of ethane
(ii)
Step 1: Initiation
Cl2---------> Cl* +Cl*
Ultraviolet light breaks down the chlorine molecule into two chlorine atoms.
Step 2: Propagation
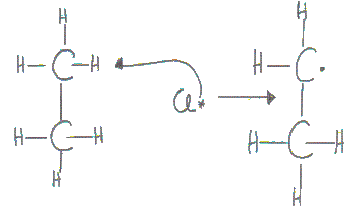
One chlorine atom attacks the ethane molecule to form hydrogen chloride and a ethyl free radical.
Step 3:
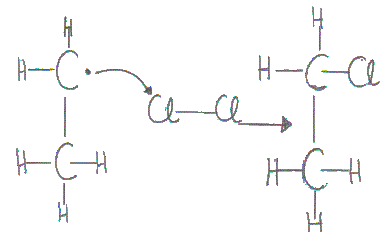
The ethyl free radical attacks another chlorine molecule to form chloroethane and another chlorine atom.
Step 4: Termination
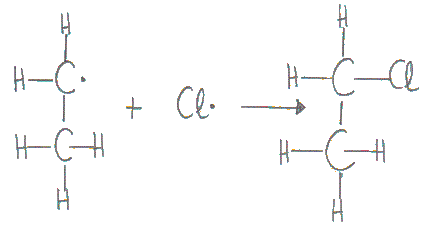
The free radicals combine to form molecules and this causes the reactions to come to an end.
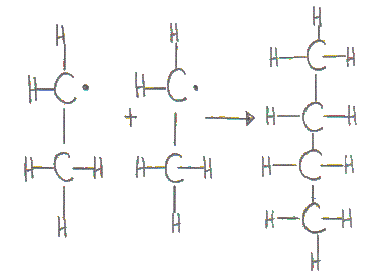
(iii) Small traces of butane can be found because of the combination of two ethyl free radicals.
Ethene

(b)

(c)
Test for unsaturation
- Add a few drops of bromine to each sample.
- Shake the test tubes.
- Sample B will turn colourless because it is unsaturated. Sample C will remain brown because it is saturated.
(d)
(i) Substitution -> monochlorination of ethane
(ii)
Step 1: Initiation
Cl2---------> Cl* +Cl*
Ultraviolet light breaks down the chlorine molecule into two chlorine atoms.
Step 2: Propagation
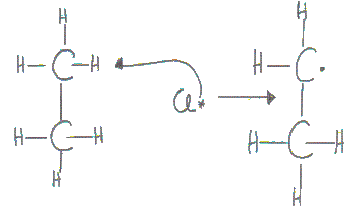
One chlorine atom attacks the ethane molecule to form hydrogen chloride and a ethyl free radical.
Step 3:
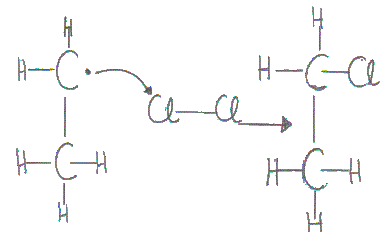
The ethyl free radical attacks another chlorine molecule to form chloroethane and another chlorine atom.
Step 4: Termination
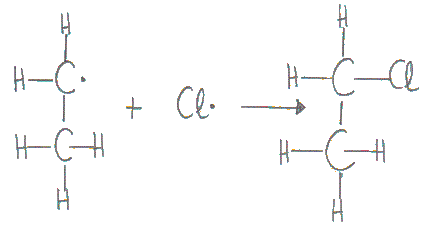
The free radicals combine to form molecules and this causes the reactions to come to an end.
(iii) Small traces of butane can be found because of the combination of two ethyl free radicals.

