Question
- Leaving Cert. Biology (Higher) 2016: Q15
- Back to the question >
Answer
(a)
(i)
Transverse section of a human vein: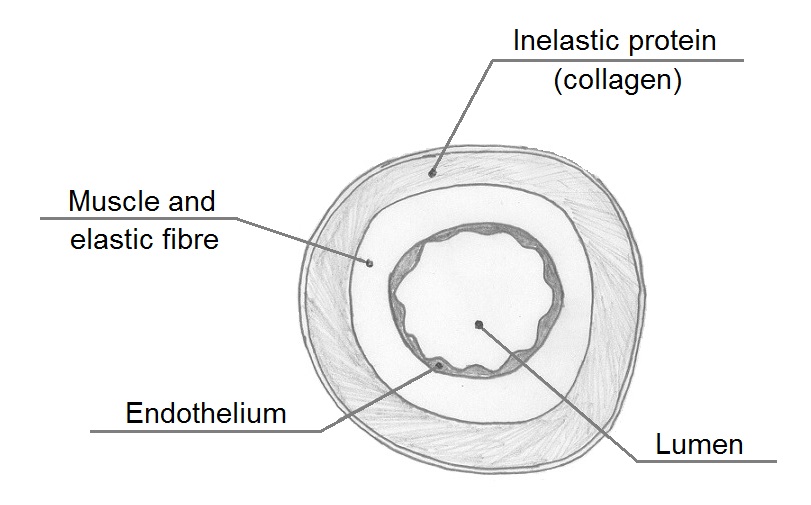
(ii)
- Cardiac vein
- Renal vein
- Pulmonary vein
- Vena cava
- Hepatic portal vein
(iii) The blood in veins is under much less pressure than arteries so it needs other methods to get back to the heart. Physical activity helps to push blood back to the heart. When muscles contract they squeeze the veins and the blood is squeezed back to the heart. Valves in the veins also prevent the backflow of blood.
(b)
(i)
- Days 1-5: The endometrium breaks down.
- Day 14: The Graafian follicle bursts releasing the egg from the ovary.
(ii) FSH and LH are produced in the pituitary gland.
(iii)
Role of FSH: It stimulates the egg to develop.
Role of LH: It causes ovulation.
(iv) Oestrogen and progesterone
(v) Function of progesterone: Progesterone produced by the corpus luteum ensures the endometrium remains in place (in case the egg is fertilised).
(c)
(i)
Red bone marrow produces blood cells.
Yellow bone marrow stores fat.
(ii)
- Scurvy: Bleeding gums or bleeding under the skin.
- Colour blindness: Inability to distinguish certain colours.
- Hyperthyroidism: Bulging eyes, loss of weight, anxiety and irritability.
- AIDS: Inability to fight infection.
(iii)
1. The use of micro-organisms in waste management
Micro-organisms break down the waste matter before it is released into the rivers or seas where it could cause problems like eutrophication. The micro-organisms break the waste down into carbon dioxide and water, which will not affect the environment.
2. Vaccination
When a very small amount of a disease or pathogen is introduced into the body it triggers an immune response. The memory cells will remember this pathogen if the body is infected again and the response to kill the disease will be much faster.
3. The artificial propagation of flowering plants
There are different methods of propagating flowering plants but the biological basis for doing so is that you know what type of plant you will produce. This is similar to asexual reproduction — taking a cutting or grafting does not lead to any variation in the new plant. If you want the plant to have the exact same flower or fruit then artificial propagation is ideal. It is also quicker than waiting for a seed to grow.
4. Increasing the amount of wholegrain foods in the diet
Wholegrain foods are not digested, so they add bulk to the waste in the large intestine. This aids peristalsis, prevents constipation and cleans out the large intestine. This helps prevent colon cancer.
