Question
- Leaving Certificate Biology (Higher) 2021: Q11
- Back to the question >
Answer
(a)
(i)
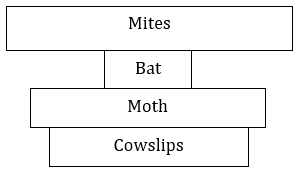
(ii) Limitation: They are often difficult to draw to scale. (Alternative answer: they do not take into account the size of the organism.)
(b)
(i) Advantage: There will be more insects in summer than in spring. This gives a better food supply to feed their offspring, which means they are more likely to survive. (Alternative answer: both day and night temperatures are warmer in summer than in spring. This means there is less chance of a sudden cold spell, which might kill the young bats.)
(ii) Bats generally roost in undisturbed places. As man develops such places for new housing and industry, bats have fewer places to roost and breed, which causes their populations to decline. (Alternative answer: the use of pesticides by humans on crops and gardens kills the insects on which bats feed. Less food means that fewer of their offspring will survive, causing their population to decline.)
(iii)
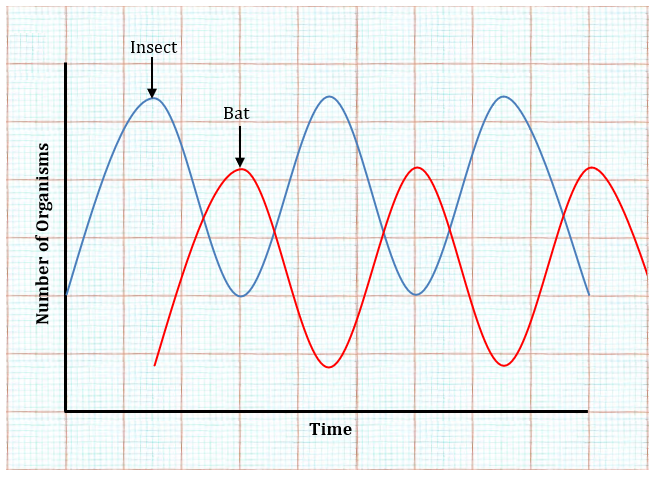
(iv) Type of adaptation: Structural adaptation (Alternative answer: behavioral adaptation)
(v) Adaptations:
- Bats have their young in early summer rather than spring, which increases their chance of survival.
- Bats navigate by echolocation, which allows them to find food in the dark.
(c)
(i) The conservation of species is the wise management of a species so that it has the food and habitat required to survive.
(ii) An example of a conservation practice used in agriculture is ‘set- aside’. Many of our pollinating insects are in decline, which is a problem because we need them to pollinate many of the foods we grow. Pollinators are in decline because of habitat loss due to recent farming practices such as the use of silage rather than hay, and the use of wire fences rather that hedgerows. Many farmers now ‘set-aside’ a portion of their farmland to grow wild. This allows the wildflowers to grow, which provides food and shelter for the pollinators and other insects. This in turn provides food for birds and small mammals. In this way habitats are restored. Farmers are paid for this new type of land use.
(iii)
1. An advantage of regular animal surveys is that they allow us to see the effect of certain activities on a population of animals, for example, the effect of a new housing development on a population of bats.
2. To estimate the number of field mice in a grassland habitat:
- Place 10 mammal traps at various locations in the grassland.
- The next morning, count, mark and release all the mice caught. (Marks should be non-toxic and should not alert predators to the mice. For example, cut a piece of fur behind the right hind leg.) The number of mice caught is called C1st.
- A week later, repeat at the same locations.
- Count the number of mice caught, (this is called C2nd), and the number of mice with your mark, (this is called M2nd).
- Using the following formula, calculate the population of mice: Pop. of Mice = (C1st x C2nd) / M2nd
